Calculating the Products of Monochlorination
Calculating the Products of Monochlorination
The monochlorination and bromination of alkanes is an important step for creating building blocks for organic synthesis. It is the basic approach to functionalize alkanes. For example, monochlorination of butane to 2-chorobutane may be used in Grignard synthesis of alcohols. It can be used to carry out several other well-known reactions of alkyl halides.
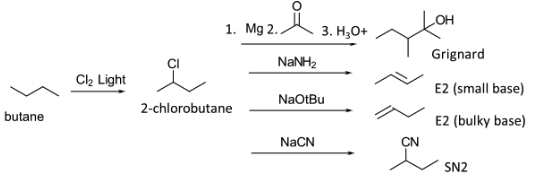
Chlorination and bromination is by a radical process that gives products based on the reactivity of the hydrogen atoms. It is well-known that 1o, 2o, and 3o hydrogens react at different rates. The relative rates for chlorine and bromine are given in the table.
Table of Relative Rates
| Relative Rate | 1° | 2° | 3° |
| Chlorination | 1 | 3.8 | 5.0 |
| Bromination | 1 | 82 | 1600 |
The relative rates may be used to calculate the percent yield of each chlorination or bromination product by the formula:
% yield = (% isomer)/(Sum of all % isomers) x 100
% Isomer = Number of H x relative rate
Consider the following reaction of propane with chlorine under radical reaction conditions as an example. What are the products and percent yields of the monochlorination products of propane based on the following reaction.
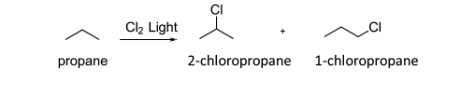
The solution:
1-chloropropane = 6 H × 1.0 = 6.0
2-chloropropane = 2 H × 3.8 = 7.6
yield % of 1-chloropropane = 6.0/(6.0+7.6) = 44%
yield % of 1-chloropropane 7.6/(6.0+7.6) = 56%